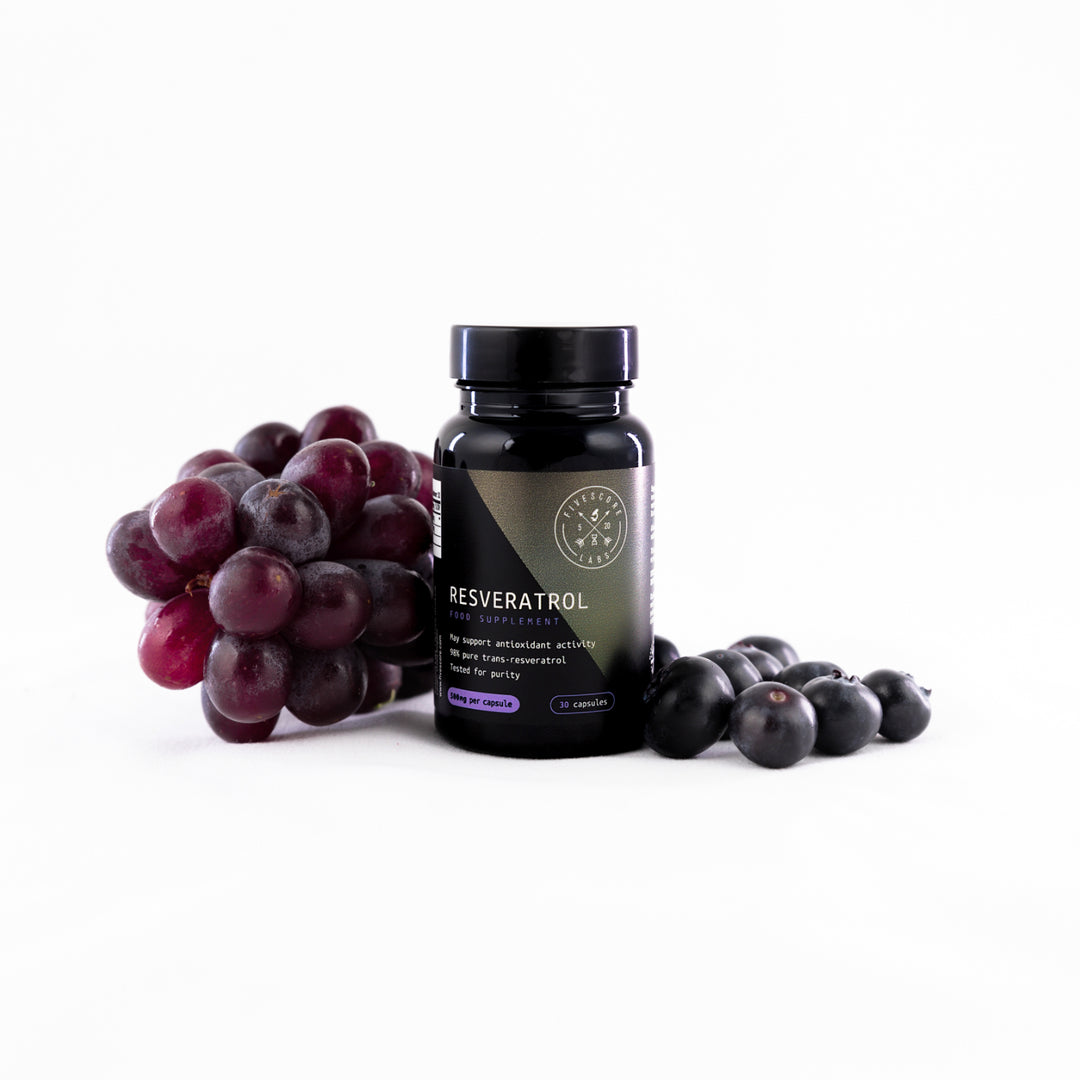
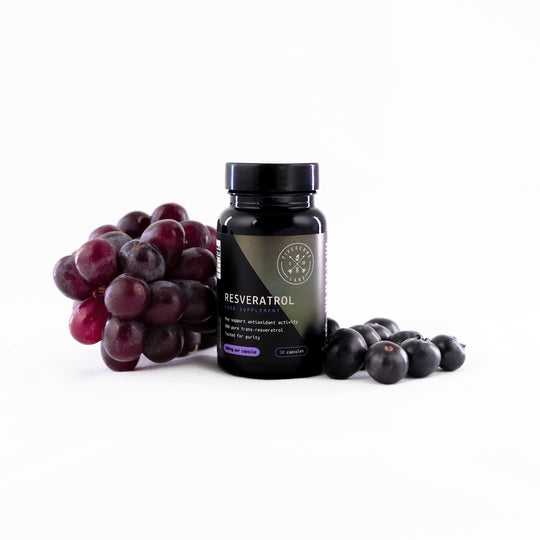
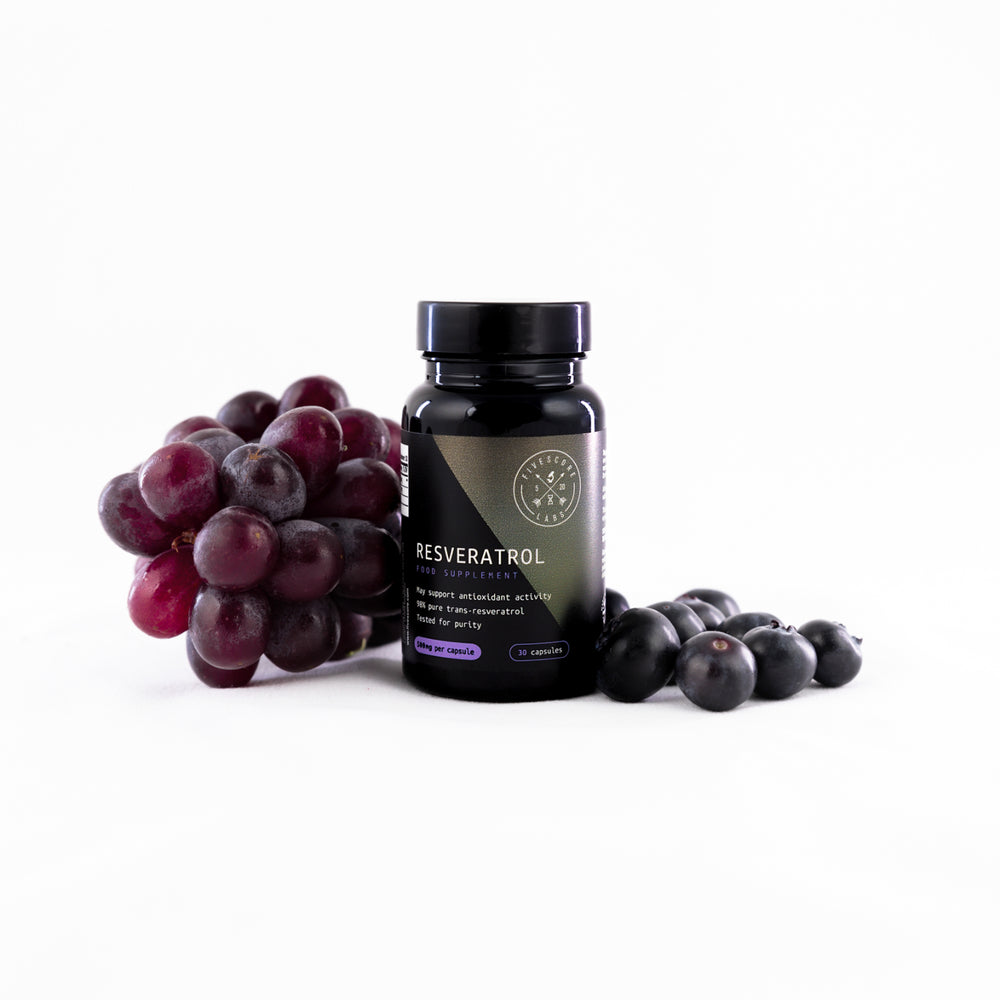
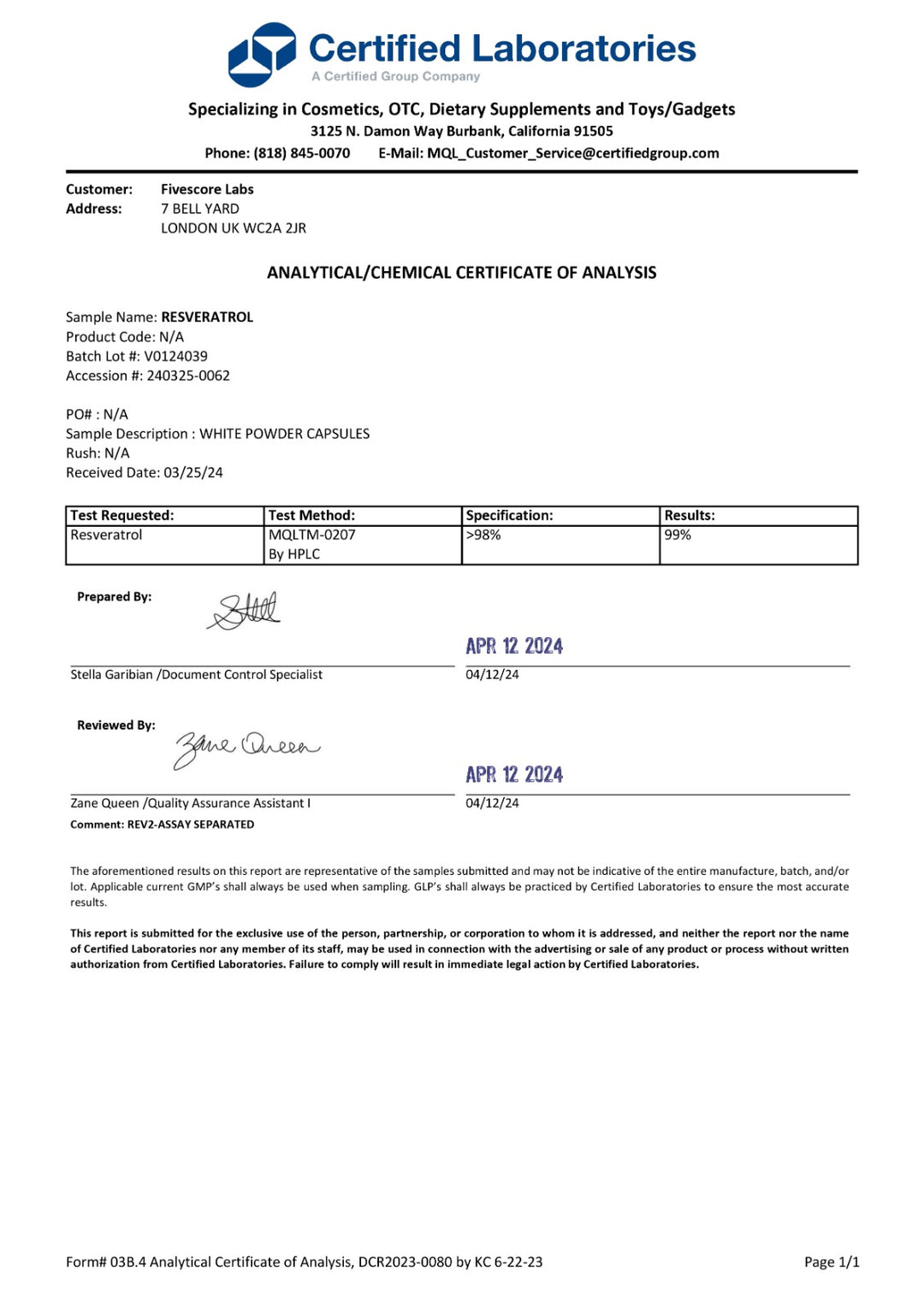
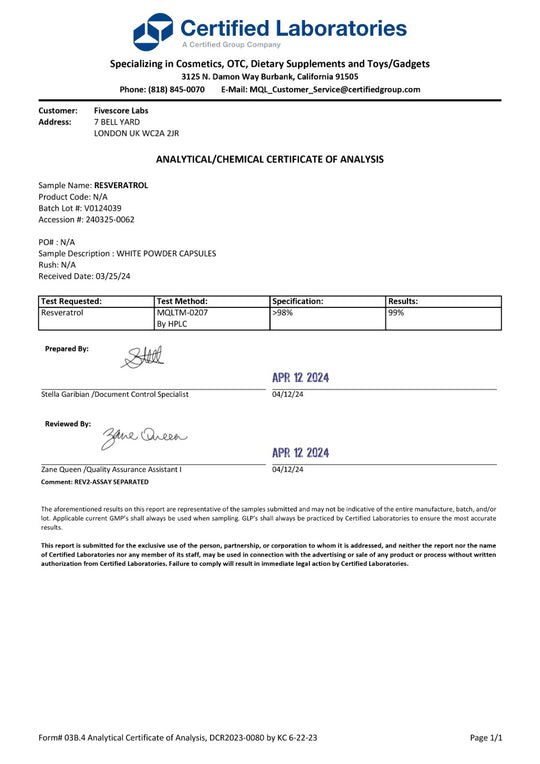
ريسفيراترول فائق النقاء - نقي بنسبة 98٪ (تم اختباره في معمل خارجي)
- Discounted shipping options for bundle orders
- In stock, ready to ship
- Backordered, shipping soon
✔️ULTRA HIGH PURITY AND OPTIMUM ABSORPTION. Our 98% pure Resveratrol has unrivalled bioavailability, research shows that micronized Resveratrol is absorbed several times more effectively than standard resveratrol. Due to its size, micronized Resveratrol can pass through cellular structures, maximizing potency on a microscopic level.
✔️SUPER ANTIOXIDANT ACTION, IMMUNE & HEALTHSPAN SUPPORT. Resveratrol is a polyphenolic compound, naturally found in red grapes, blueberries and other foods. Resveratrol has recently received a large amount of attention due to scientific research indicating the antioxidant properties of the compound.
✔️3RD PARTY LAB TESTED FOR PURITY. Our Resveratrol is one of the few on the market independently verified for purity. Our latest batch is at least 98% pure.
✔️UK MADE & AT THE HIGHEST GMP STANDARD FACILITIES. This product is manufactured in the UK to the highest GMP standards, ensuring potency and purity.
✔️100% VEGAN WITH NO FILLERS, BINDERS OR ADDITIVES. At Fivescore Labs, we believe in transparency which is why you won’t find any nasty stuff in our products including any fillers, binders or additives, unlike some of our competitors.
Resveratrol belongs to a group of compounds known as stilbenes. It is a phytoalexin, a type of antibiotic produced by plants to protect against infections. This compound has two isomeric forms: cis-resveratrol and trans-resveratrol, with the latter being the more biologically active and stable form. Trans-resveratrol is the form most commonly found in dietary supplements and has been the subject of extensive research.
It has gained significant attention for its potential health benefits, especially for its antioxidant properties. As an antioxidant, resveratrol helps protect the body's cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can lead to cellular damage and contribute to aging and various diseases.
Upon ingestion, resveratrol is absorbed through the intestines and enters the bloodstream. However, its bioavailability can be relatively low due to rapid metabolism and elimination. Despite this, resveratrol may exert its beneficial effects at the cellular level, in particular when it is ingested with food as it is a fat soluble compound.
Resveratrol's primary role in the body is as an antioxidant. It helps neutralize free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing damage to cellular structures, including DNA, proteins, and lipids. This function may be important in protecting the body from various chronic conditions, including heart disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Resveratrol has been shown to potentially inhibit the activity of enzymes and molecules involved in inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a common underlying factor in many diseases, and by reducing inflammation, resveratrol may help mitigate the risk of these conditions.
Resveratrol may also potentially support cardiovascular health by helping improve the function of blood vessels, helping reduce blood pressure, and helping decrease LDL cholesterol levels.
When incorporating resveratrol into your daily regimen, it is important to consider the form and dosage to maximize its benefits.
- Supplement Form: Resveratrol is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. The most effective supplements contain trans-resveratrol, as this form is more readily utilized by the body.
- Dosage: The appropriate dosage of resveratrol can vary based on individual health needs and goals. Common dosages range from 250 mg to 1 g per day. It is advisable to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Timing and Absorption: Resveratrol supplements can be taken with or without food. However, some studies suggest that taking resveratrol with a meal containing fat may enhance its absorption. To ensure optimal absorption and effectiveness, consider taking resveratrol at the same time each day.
- Potential Interactions: While resveratrol is generally considered safe, it can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs. If you are on medication or have a chronic health condition, consult your healthcare provider before starting resveratrol supplementation.
Resveratrol is a powerful antioxidant with potential health benefits. By incorporating resveratrol into your daily routine, it may help support the body's defense against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cardiovascular issues, while promoting overall antioxidant protection. Always choose high-quality supplements and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your individual needs. Please remember, the most crucial component of longevity is a balanced approach encompassing a varied diet, regular exercise and sleep hygiene.
These statements have not been evaluated by any official health authority. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
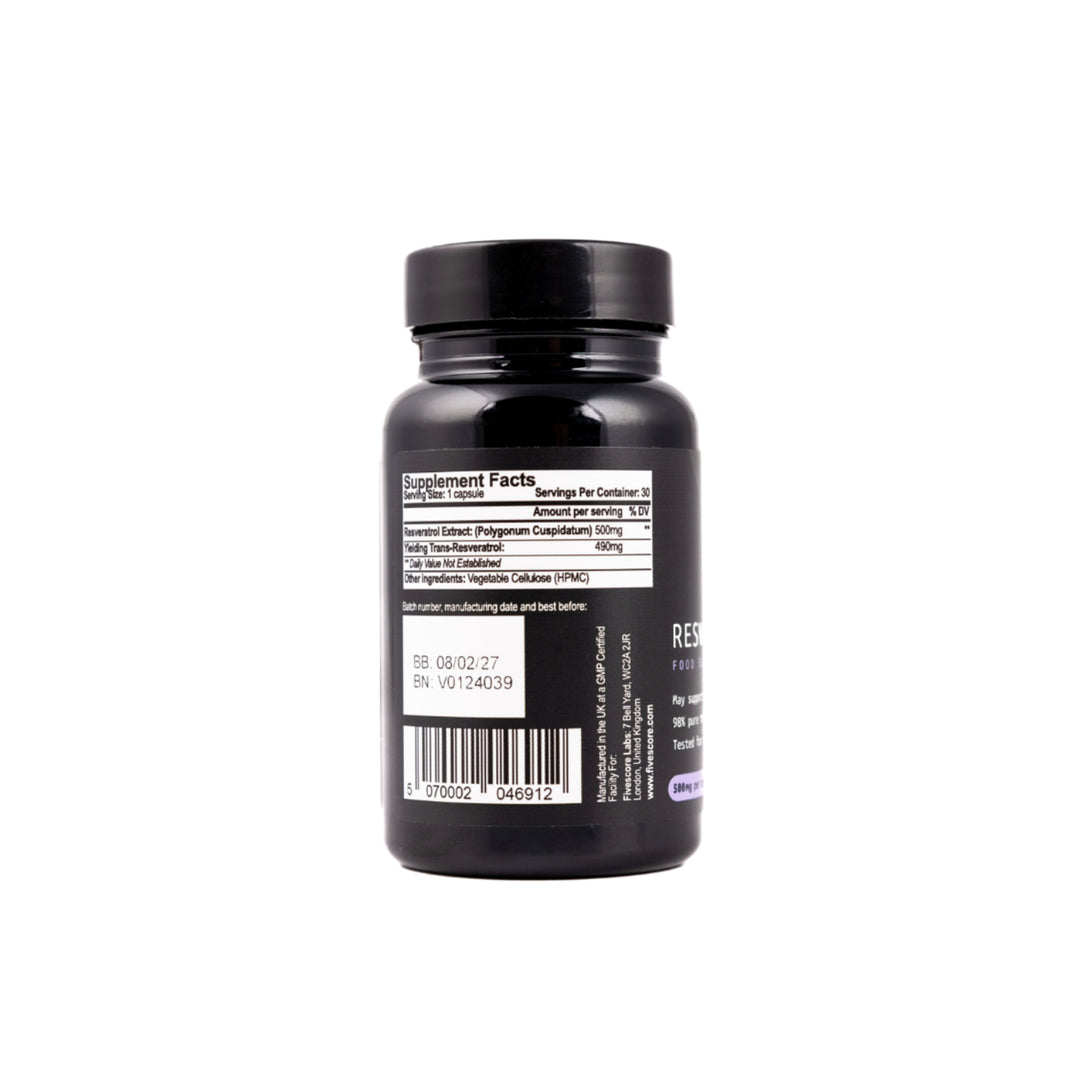
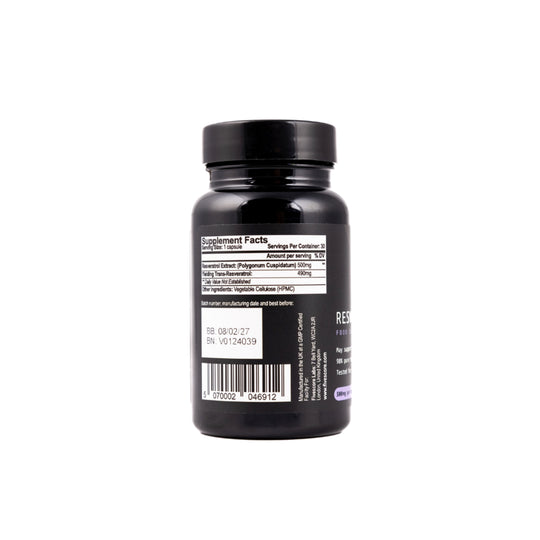
Typical amount per capsule:
Per Capsule: 500mg 98% Resveratrol – providing 490mg natural trans-Resveratrol.
Capsule Shell: Vegan friendly HPMC.
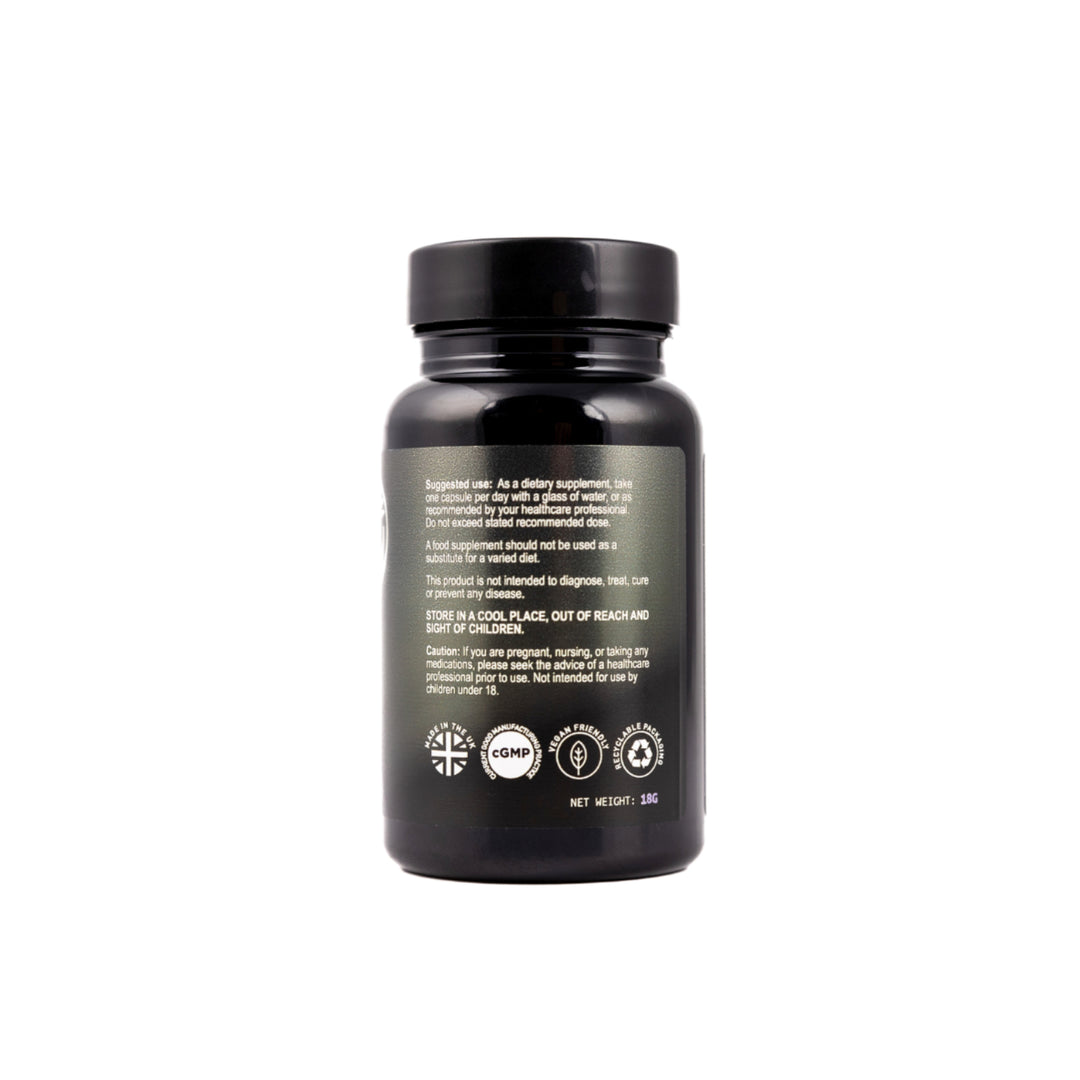
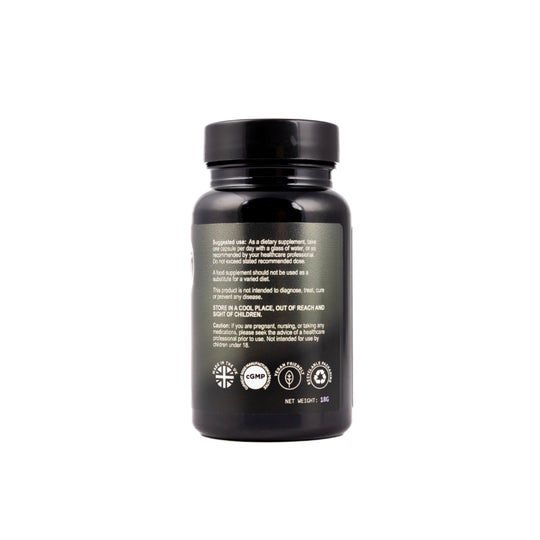
Suggested use:
As a food supplement for adults: Take 1 capsule daily with food, or as directed by a healthcare practitioner. Do not exceed the stated recommended daily dose.
Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a healthy and varied diet. You need to follow a healthy diet, exercise routine and sleep habit in order to benefit from long term health.
Resveratrol regulates neuro-inflammation and induces adaptive immunity in Alzheimer's disease
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of resveratrol for Alzheimer disease
Resveratrol supplementation improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Evidence for a Common Mechanism of SIRT1 Regulation by Allosteric Activators